Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss or even blindness.

Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease and a leading cause of blindness. It is caused by changes in the blood vessels of the retina.
In diabetic retinopathy- blood vessels may swell and leak fluid, abnormal new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina.
If you have diabetic retinopathy, at first you may not notice changes to your vision. But over time, diabetic retinopathy can get worse and cause vision loss. Diabetic retinopathy usually affects both eyes.
Diabetic retinopathy has four stages:
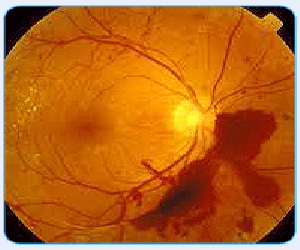
Proliferative Retinopathy

Proliferative Retinopathy
How does diabetic retinopathy cause vision loss?
Blood vessels damaged from diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss in two ways:
Who is at risk for diabetic retinopathy?
If you have diabetes get a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year and remember:
Whether or not you have symptoms, early detection and timely treatment can prevent vision loss.
If you have diabetic retinopathy, you may need an eye exam more often. People with proliferative retinopathy can reduce their risk of blindness by 95 percent with timely treatment and appropriate follow-up care.
Does diabetic retinopathy have any symptoms?
Often there are no symptoms in the early stages of the disease, nor is there any pain.Don't wait for symptoms. Be sure to have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year.
Blurred vision may occur when the macula—the part of the retina that provides sharp central vision—swells from leaking fluid. This condition is called macular edema. If new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina, they can bleed into the eye and block vision.
What are the symptoms of proliferative retinopathy if bleeding occurs?
At first, you will see a few specks of blood, or spots, "floating" in your vision. You may need treatment before more serious bleeding occurs. Hemorrhages tend to happen more than once, often during sleep.
Sometimes, without treatment, the spots clear, and you will see better. However, bleeding can reoccur and cause severely blurred vision.
If left untreated, proliferative retinopathy can cause severe vision loss and even blindness. Also, the earlier you receive treatment, the more likely treatment will be effective.
How are diabetic retinopathy and macular edema detected?
Diabetic retinopathy and macular edema are detected during a comprehensive eye exam that includes:
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
During the first three stages of diabetic retinopathy, no treatment is needed, unless you have macular edema. To prevent progression of diabetic retinopathy, people with diabetes should control their levels of blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol.
Proliferative retinopathy is treated with laser surgery. This procedure is called scatter laser treatment. Scatter laser treatment helps to shrink the abnormal blood vessels. Laser burns in the areas of the retina away from the macula, causing the abnormal blood vessels to shrink.
Because a high number of laser burns are necessary, two or more sessions usually are required to complete treatment. Although you may notice some loss of your side vision, scatter laser treatment can save the rest of your sight. Scatter laser treatment may slightly reduce your color vision and night vision.
If the bleeding is severe, you may need a surgical procedure called a vitrectomy. During a vitrectomy, blood is removed from the center of your eye.
How is a macular edema treated?
Macular edema is treated with laser surgery. This procedure is called focal laser treatment. Your doctor places up to several hundred small laser burns in the areas of retinal leakage surrounding the macula. These burns slow the leakage of fluid and reduce the amount of fluid in the retina. The surgery is usually completed in one session. Further treatment may be needed.
A patient may need focal laser surgery more than once to control the leaking fluid. If you have macular edema in both eyes and require laser surgery, generally only one eye will be treated at a time, usually several weeks apart. Focal laser treatment stabilizes vision. In fact, focal laser treatment reduces the risk of vision loss by 50 percent. In a small number of cases, if vision is lost, it can be improved. Contact your eye care professional if you have vision loss.
What happens during laser treatment?
Both focal and scatter laser treatment are performed in your doctor's office or eye clinic. The lights in the office will be dim. As you sit facing the laser machine, your doctor will hold a special lens to your eye. During the procedure, you may see flashes of light. These flashes eventually may create a stinging sensation that can be uncomfortable. You will need someone to drive you home after surgery. Because your pupil will remain dilated for a few hours, you should bring a pair of sunglasses.
For the rest of the day, your vision will probably be a little blurry. If your eye hurts, your doctor can suggest treatment.
Laser surgery and appropriate follow-up care can reduce the risk of blindness by 90 percent. However, laser surgery often cannot restore vision that has already been lost. That is why finding diabetic retinopathy early is the best way to prevent vision loss.
What is a vitrectomy?
If you have a lot of blood in the center of the eye (vitreous gel), you may need a vitrectomy to restore your sight. If you need vitrectomies in both eyes, they are usually done several weeks apart.
A vitrectomy is performed under either local or general anesthesia. Through a tiny incision, a small instrument is used to remove the vitreous gel that is clouded with blood. The vitreous gel is replaced with a salt solution. Because the vitreous gel is mostly water, you will notice no change between the salt solution and the original vitreous gel. You will probably be able to return home after the vitrectomy. Some people stay in the hospital overnight. Your eye will be red and sensitive. You will need to wear an eye patch for a few days or weeks to protect your eye. You also will need to use medicated eyedrops to protect against infection.
What can I do if I already have lost some vision from diabetic retinopathy?
If you have lost some sight from diabetic retinopathy, ask your eye care professional about low vision services and devices that may help you make the most of your remaining vision. Ask for a referral to a specialist in low vision. Many community organizations and agencies offer information about low vision counseling, training, and other special services for people with visual impairments
© 2015 Drushti Eye Institute Pvt Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Developed by - Regal Soft India